The fastest 2.4 GHz channel typically depends on local interference and network congestion, but generally, channels 1, 6, and 11 are the best choices because they don’t overlap. Among these, channel 6 is often considered optimal because it usually provides the clearest signal, especially when multiple networks are nearby. In essence, selecting a less congested channel can significantly improve your Wi-Fi speed and reliability.
The fastest 2.4 GHz channel is usually channel 6, but the best choice can vary based on your environment. To find the ideal channel, use Wi-Fi analyzer tools to identify the least crowded options around you. Understanding these nuances helps ensure smoother internet experiences, especially in crowded or urban areas.
If you’re wondering which 2.4 GHz channel offers the best speed, local interference and channel congestion are key factors. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the main non-overlapping options, with channel 6 often being the most reliable for optimal performance. By choosing the right channel, you can reduce interference and enjoy faster, more stable Wi-Fi connections.
Which 2.4 GHz Channel is Fastest?
Understanding 2.4 GHz Channels
The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi band is a popular choice for many homes and small offices because it offers good coverage. It operates on multiple channels that overlap, which can cause interference. These channels are numbered from 1 to 14, but not all are available everywhere. Knowing which channel is fastest helps you get better Wi-Fi performance.
How Wi-Fi Channels Work
Each Wi-Fi channel in the 2.4 GHz band covers a specific frequency range. The channels are spaced 5 MHz apart, but since each channel’s bandwidth is 20 MHz, they often overlap. Overlapping channels can interfere with each other, slowing down your network. To avoid this, it’s best to choose a channel that doesn’t overlap nearby channels.
Which 2.4 GHz Channel Offers the Highest Speed?
The fastest 2.4 GHz channel depends on several factors. In theory, all non-overlapping channels—channels 1, 6, and 11—offer the best speed because they don’t interfere. However, actual speed also depends on other factors like Wi-Fi congestion. Typically, selecting one of these non-overlapping channels minimizes interference and maximizes throughput.
Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speed on 2.4 GHz
Speed variations happen based on:
- Network congestion from nearby Wi-Fi networks
- Physical barriers like walls or furniture
- Number of devices connected
- Router quality and settings
- Interference from other electronic devices
Choosing the right channel becomes even more crucial when many networks are nearby.
Why Channels 1, 6, and 11 Are Special
These channels are considered non-overlapping in the 2.4 GHz band, which means they don’t interfere with each other. Using one of these channels reduces the chance of data collision and improves speed. In many cases, switching to one of these channels can significantly boost your Wi-Fi performance.
How to Find the Fastest 2.4 GHz Channel in Your Area
To pick the best channel, you need to analyze your Wi-Fi environment. Use tools like Wi-Fi analyzers or apps on your smartphone or computer. These tools scan nearby networks and show which channels are least crowded. Selecting the least congested channel can result in faster, more stable Wi-Fi.
Using Wi-Fi Analyzer Tools
Wi-Fi analyzer apps show:
- Signal strength of nearby networks
- Which channels they are using
- Interference levels on each channel
Popular options include NetSpot, Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android), and AirPort Utility (iOS). These tools simplify finding the best channel for your location.
Manual vs. Automatic Channel Selection
Some routers automatically select the least congested channel, but this feature isn’t always perfect. Manual selection involves scanning your environment to identify the best channel. Many users prefer manual setup for precise control, especially if they notice persistent Wi-Fi speed issues.
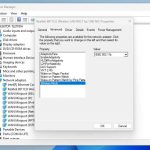
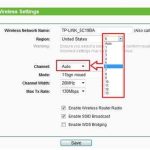
Steps to Manually Choose the Fastest Channel
Follow these steps:
- Open your Wi-Fi analyzer app and scan your environment.
- Identify which channels are least crowded with nearby networks.
- Log into your router’s admin settings.
- Navigate to the wireless settings section.
- Change the channel to one of the identified least congested options (preferably 1, 6, or 11).
- Save changes and test your Wi-Fi speed.
Repeating this process periodically can help maintain optimal Wi-Fi performance.
Impact of Router Placement on Channel Effectiveness
Even with the best channel selection, placement affects speed. Place your router in a central location, away from thick walls or electronic devices that cause interference. Proper placement combined with optimal channel choice can double your Wi-Fi speed.
Related Topics: Frequency Band and Dual-Band Routers
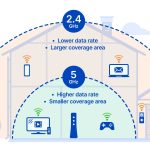
Many modern routers support dual-band technology, offering both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Since 5 GHz channels are less crowded and faster, consider using this band for high-speed needs. If sticking to 2.4 GHz, selecting the right channel with minimal interference is key.
Summary of Recommended 2.4 GHz Channels for Speed
- Channels 1, 6, and 11 are best for avoiding overlap.
- Use Wi-Fi analyzer tools to determine least congested channels in your area.
- Switch to an optimal channel if your Wi-Fi is slow or unstable.
- Regularly monitor network environment for changes in interference patterns.
In most environments, **channels 1, 6, and 11** will provide the best speed for 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. However, actual performance depends on your surroundings, device density, and interference sources. Regularly checking your Wi-Fi environment and adjusting your channel can help maintain fast and reliable connections. Remember, combining proper channel selection with good router placement and device management improves your network’s overall speed and stability.
What Is The Difference Between 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz WiFi
Frequently Asked Questions
How does interference affect the speed of different 2.4 GHz channels?
Interference from other wireless devices and appliances operating on similar frequencies can slow down specific channels. Channels with less congestion tend to provide faster connection speeds. Selecting a channel with minimal interference ensures better performance for your Wi-Fi network.
Are some 2.4 GHz channels less crowded than others?
Yes, certain channels are less crowded depending on your location and the surrounding devices. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are typically recommended because they don’t overlap with each other, reducing interference and improving speed. Conducting a scan to identify the least congested channel helps optimize your network speed.
Can adjusting your router’s channel improve overall Wi-Fi speed?
Adjusting your router’s channel can significantly enhance your Wi-Fi performance, especially if your current channel experiences congestion. By selecting a less crowded channel, you reduce interference and achieve faster, more stable connections across devices.
Does the ability of a channel to support higher data rates depend on its frequency?
While all 2.4 GHz channels support similar maximum data rates, practical speed depends on factors like interference and signal quality. Choosing a channel with less noise allows your devices to communicate more efficiently, resulting in better overall speeds.
Is there a way to determine which 2.4 GHz channel is the fastest in my environment?
Yes, you can use Wi-Fi analyzer tools to scan your area and identify the least congested channels. These tools visualize network activity, helping you select the channel that offers the best potential speed and stability for your Wi-Fi network.
Final Thoughts
The fastest 2.4 GHz channel depends on your environment and interference levels. Generally, channels 1, 6, and 11 are optimal because they do not overlap. In less congested areas, these channels deliver better speeds and stability.
However, in crowded spaces, switching between these channels can improve performance. Testing different channels helps identify which works best for your setup.
Which 2.4 GHz channel is fastest? The answer varies, but many find channel 6 offers the best speed with minimal interference.