**Quick answer:** dBm in Wi-Fi signals measures the strength of the wireless signal, indicating how powerful or weak it is. A higher (less negative) dBm value means a stronger connection, while a lower (more negative) value signals a weaker one.
Knowing what dBm means in Wi-Fi can seem confusing at first, but it’s actually quite straightforward. Think of dBm as a way to gauge how well your device is communicating with your router — the higher the number, the better your signal. Whether you’re troubleshooting slow internet or trying to position your router for optimal coverage, understanding dBm helps you get the most out of your wireless connection. In this article, we’ll explore what dBm really indicates, how to interpret its values, and why it matters for your Wi-Fi experience. So, if you’ve ever wondered how to tell if your Wi-Fi is strong enough, keep reading!
What is dBm in Wi-Fi Signal?
Understanding what dBm means in Wi-Fi signals helps you know how strong your Wi-Fi connection really is. It is a measurement that tells us the power level of the wireless signal coming from your router or access point. The strength of the Wi-Fi signal impacts how fast and reliable your internet connection will be.
What Does dBm Stand For?
The abbreviation dBm stands for decibels relative to one milliwatt. It is a unit used to express the power level of radio signals, including Wi-Fi signals. The dBm scale is logarithmic, which means each increase of 3 dBm roughly doubles the power, making it easier to compare different signal strengths.
Why Is dBm Important for Wi-Fi?
Knowing the dBm value helps you understand how well your device can communicate with the Wi-Fi router. A higher (less negative) dBm value indicates a stronger signal, leading to better connection quality. Conversely, a lower (more negative) dBm value suggests a weaker signal that might cause slow browsing or disconnections.
Typical dBm Values in Wi-Fi Signals
Wi-Fi signals usually fall within a certain range of dBm values. Here are some common examples:
- -30 dBm: Excellent signal strength, very close to the source. Usually found right next to the router.
- -50 dBm: Very good signal, capable of supporting high-speed internet and streaming.
- -60 dBm: Good signal, suitable for most online activities.
- -70 dBm: Fair signal, may result in slower speeds and buffering.
- -80 dBm: Weak signal, connection might be unreliable.
- -90 dBm or lower: Very poor signal, likely to cause disconnections.
Understanding the Logarithmic Scale
The dBm scale is logarithmic, which means small changes can reflect significant differences in signal strength. A change from -60 dBm to -50 dBm signals an increase in power by about 10 times. This scale helps users understand the magnitude of signal differences clearly and efficiently.
How dBm Affects Wi-Fi Performance
The strength of your Wi-Fi signal directly influences your internet speed, latency, and overall network stability. Strong dBm signals enable faster download and upload speeds with minimal lag. Weak signals often lead to buffering videos, interrupted calls, and sluggish browsing.
Measuring Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Tools and Methods
Built-in Device Tools
Most smartphones, tablets, and laptops have built-in features or apps to check Wi-Fi signal strength and dBm levels. These tools display the signal in real-time, helping you optimize your router placement.
Wi-Fi Analyzers and Apps
Specialized apps like NetSpot, Wi-Fi Analyzer, and Acrylic Wi-Fi provide detailed reports of Wi-Fi signal strengths. They can display dBm levels for different access points and help identify dead zones or interference sources.
What Is Considered a Good Wi-Fi Signal?
A signal strength of around -50 dBm to -60 dBm is generally regarded as good for most activities. For high-definition streaming and online gaming, signals closer to -50 dBm are ideal. Anything below -70 dBm may cause problems, especially with multiple devices connected.
Factors Influencing Wi-Fi dBm Levels
Distance from Router
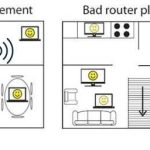
The farther you are from your Wi-Fi source, the weaker the signal becomes. Wall thickness, furniture, and other obstacles can also diminish signal strength.
Interference from Other Devices
Other wireless devices, such as cordless phones or microwave ovens, can interfere with Wi-Fi signals, reducing the dBm level and causing disruptions.
Router Quality and Placement
A high-quality router with multiple antennas can provide stronger signals. Proper placement in open, central locations also enhances Wi-Fi coverage and strength.
How to Improve Your Wi-Fi Signal Based on dBm
- Place your router in a central, elevated location away from thick walls and metal furniture.
- Reduce interference by keeping other electronic devices away from your router.
- Upgrade to a modern router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards like 802.11ac or 802.11ax.
- Use Wi-Fi range extenders or mesh networks to boost coverage in larger spaces.
- Adjust router antennas for optimal signal distribution if your model allows.
Understanding Signal Loss and Decibel Drop-Off
Path Loss and Obstructions
Signal strength drops as it travels through walls, ceilings, and furnishings. Each obstacle can cause a specific decibel loss, weakening the overall signal.
Free Space Path Loss
This is the natural decline in signal strength over distance, even without obstructions. It’s a key factor when planning Wi-Fi coverage in your home or office.
Correlation Between dBm and Data Transfer Rates
| Wi-Fi Signal Strength (dBm) | Performance Expectations | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| -30 to -50 | Excellent speeds, minimal latency | HD streaming, online gaming, large downloads |
| -50 to -60 | Good speeds, reliable connection | Standard browsing, video calls |
| -60 to -70 | Moderate speeds, occasional lag | Emails, light browsing, basic streaming |
| -70 to -80 | Poor speeds, frequent interruptions | Basic browsing, low-bandwidth tasks |
| -80 and below | Very slow or no connection | Impossible to use effectively |
Summary of Key Points about dBm in Wi-Fi
In summary, dBm measures Wi-Fi signal strength and influences network performance. Signals closer to -30 dBm are ideal, providing fast and reliable internet. As signal strength decreases, performance and stability get worse, especially below -70 dBm.
By monitoring and optimizing your dBm levels, you can significantly improve your Wi-Fi experience. Proper placement, interference reduction, and equipment upgrades are some of the most effective ways to maintain strong signal levels, ensuring a better online experience for all your devices.
12 – Understanding Signal Strength in mW and dBm
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the dBm level affect Wi-Fi connectivity quality?
The dBm level indicates the strength of a Wi-Fi signal. Higher dBm values, closer to 0, represent stronger signals that typically provide faster speeds and more reliable connections. Conversely, lower dBm values mean weaker signals, which can lead to slower data transfer, increased latency, and dropped connections. Maintaining an optimal dBm level ensures consistent and efficient Wi-Fi performance.
What is considered a good dBm range for stable Wi-Fi signals?
A good dBm range for stable Wi-Fi signals generally falls between -30 dBm and -60 dBm. Signals within this range tend to offer reliable connectivity suitable for most activities, including streaming, gaming, and browsing. Signals weaker than -70 dBm might cause interruptions, while those stronger than -30 dBm are usually near the access point, which can sometimes cause interference.
Why does the Wi-Fi signal strength fluctuate in dBm over time?
Wi-Fi signal strength fluctuates in dBm due to various factors such as physical obstructions, distance from the router, interference from other electronic devices, and network congestion. These variables can cause temporary decreases or increases in signal strength, affecting overall connection quality. Monitoring and optimizing your environment can help stabilize the signal level.
Final Thoughts
What is dBm in Wi-Fi signal? It measures the strength of a wireless signal, helping users understand connection quality. A higher dBm value indicates a stronger signal, resulting in better performance. Conversely, lower values suggest weaker signals and potential connectivity issues. Knowing dBm levels allows users to optimize their Wi-Fi setup for optimal coverage and speed.